QUALITY CONTROL
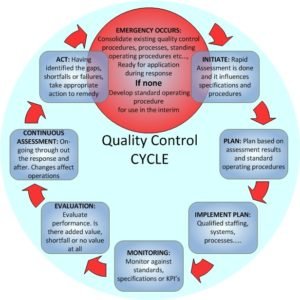
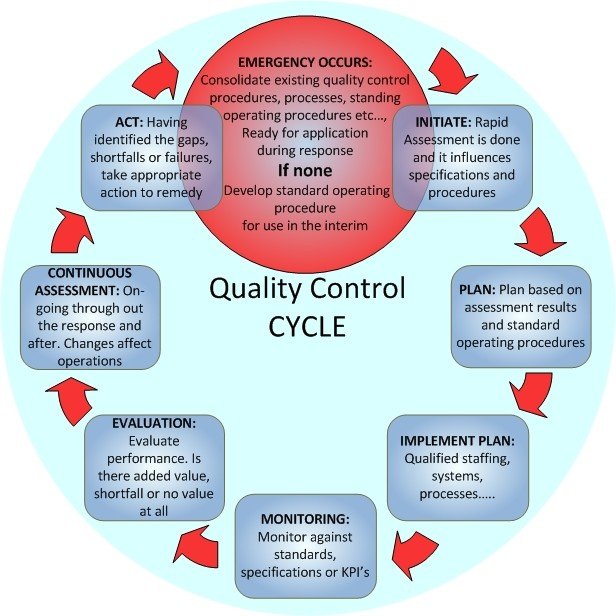
Quality control is shortly said QC, QC is a process by which things review the quality of all factors involved in production. ISO 9000 defines quality control as “A part of quality management focused on fulfilling quality requirements of customers.
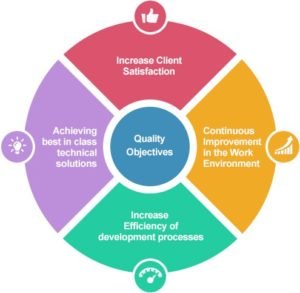
This approach places a prominence on three aspects
- Elements such as controls, job management, defined and well managed processes, performance and integrity criteria, and identification of records.
- Competence, such as knowledge, skills, experience, and qualifications
- Soft elements, such as personnel, integrity, confidence, organizational culture, motivation, team spirit and quality relationships.
Controls include product inspection, where every product is examined visually, and often using a stereo microscope for fine detail before the product is sold into the external market. Inspectors will be provided with lists and descriptions of unacceptable product defects such as cracks or surface defects for example.
The quality of the outputs is at risk if any of these three aspects is deficient in any way.
Different Approaches:
There is a tendency for individual consultants and organizations to name their own unique approaches to quality control—a few of these have ended up in worldwide use:
1930’s: Statistical quality control (SQC): The application of statistical methods (specifically control charts and acceptance sampling) to quality control
1956’s: Total quality control (TQC): Popularized by Armand V. Feigenbaum in a Harvard business review article and book of the same name. Stresses involvement of departments in addition to production (e.g., accounting, design, finance, human resources, marketing, purchasing, sales).
1960’s: Statistical Process Control (SPC): The use of control charts to monitor an individual industrial process and feedback performance to the operators responsible for that process. Inspired by control systems.
1968’s: Company-wide quality control (CWQC): Quality Control in Japanese style.
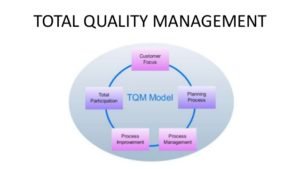
1985’s: Total Quality Management (TQM): Quality movement originating in the United States department of defence that uses (in part) the techniques of statistical quality control to drive continuous organizational improvement.
1986’s: Six Sigma (6σ): Statistical quality control applied to business strategy. Initiated by Motorola.




Good
Good info.Thanks for info.
Nice content.Thanks
Good content which is worth reading. Thanks for info.
nice article with good content which is worth reading it. Thanks for info.
Best article with good info . Thanks
Good Article which is worth reading it. Thanks
The article is very informative which is worth reading it.
Very Good Article with useful content .Thanks for info
Good information which is worth reading it .Thanks