Quality Assurance:

Quality assurance is shortly known as (QA) is a way of preventing mistakes or defects in manufactured products and avoiding problems when delivering solutions or services to customers; which ISO 9001 defines as “part of quality management focused on providing confidence that quality requirements will be fulfilled”. This defect prevention in quality assurance differs subtly from defect detection and rejection in quality control, and has been referred to as a shift left as it focuses on quality earlier in the process.
Quality assurance comprises administrative and procedural activities implemented in a quality system so that requirements and goals for a product, service or activity will be fulfilled. It is the systematic measurement, comparison with a standard, monitoring of processes and an associated feedback loop that confers error prevention. This can be contrasted with quality control, which is focused on process output.
Quality assurance includes two principles: “Fit for purpose” (the product should be suitable for the intended purpose); and “right first time” (mistakes should be eliminated). QA includes management of the quality of raw materials, assemblies, products and components, services related to production, and management, production and inspection processes. The two principles also manifest before the background of developing (engineering) a novel technical product: The task of engineering is to make it work once, while the task of quality assurance is to make it work all the time.
Suitable quality is determined by product users, clients or customers, not by society in general. It is not related to cost, and adjectives or descriptors such as “high” and “poor” are not applicable. For example, a low priced product may be viewed as having high quality because it is disposable, whereas another may be viewed as having poor quality because it is not disposable.
Approaches:
Failure testing
A valuable process to perform on a whole consumer product is failure testing or stress testing. In mechanical terms this is the operation of a product until it fails, often under stresses such as increasing vibration, temperature, and humidity. This exposes many unanticipated weakness in a product, and the data is used to drive engineering and manufacturing process improvements. Often quite simple changes can dramatically improve product service, such as changing to mold-resistant paint or adding lock washer placement to the training for new assembly personnel.
Statistical control
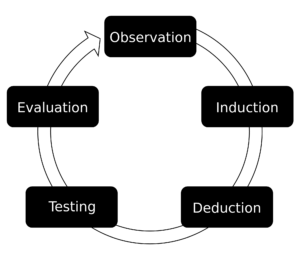
Statistical control is based on analyses of objective and subjective data.Many organizations use statistical process control as a tool in any quality improvement effort to track quality data. Any product can be statistically charted as long as they have a common cause variance or special cause variance to track.
Walter Shewart of Bell Telephone Laboratories recognized that when a product is made, data can be taken from scrutinized areas of a sample lot of the part and statistical variances are then analyzed and charted. Control can then be implemented on the part in the form of rework or scrap, or control can be implemented on the process that made the part, ideally eliminating the defect before more parts can be made like it.
Total quality management
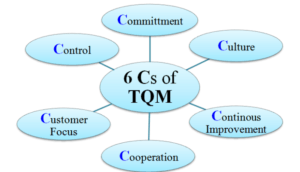
The quality of products is dependent upon that of the participating constituents, some of which are sustainable and effectively controlled while others are not. The processes which are managed with QA pertain to Total quality management.
If the specification does not reflect the true quality requirements, the product’s quality cannot be guaranteed. For instance, the parameters for a pressure vessel should cover not only the material and dimensions but operating, environmental, safety, reliability and maintainability requirements.
Models and standards
ISO 17025 is an international standard that specifies the general requirements for the competence to carry out tests and or calibrations. There are 15 management requirements and 10 technical requirements. These requirements outline what a laboratory must do to become accredited. Management system refers to the organization’s structure for managing its processes or activities that transform inputs of resources into a product or service which meets the organization’s objectives, such as satisfying the customer’s quality requirements, complying with regulations, or meeting environmental objectives. WHO has developed several tools and offers training courses for quality assurance in public health laboratories.
The Capability model maturity integration (CMMI) model is widely used to implement Process and Product Quality Assurance (PPQA) in an organization. The CMMI maturity levels can be divided into 5 steps, which a company can achieve by performing specific activities within the organization.
Company quality
During the 1980s, the concept of “company quality” with the focus on management and people came to the fore.It was considered that, if all departments approached quality with an open mind, success was possible if the management led the quality improvement process.
The company-wide quality approach places an emphasis on four aspects
- Elements such as controls, job management, adequate processes, performance and integrity criteria and identification of records
- Competence such as knowledge, skills, experiences, qualifications
- Soft elements, such as personnel integrity, confidence, organizational culture, motivation, team spirit and quality relationships.
- Infrastructure (as it enhances or limits functionality)
The quality of the outputs is at risk if any of these aspects is deficient.
QA is not limited to manufacturing, and can be applied to any business or non-business activity, including: design, consulting, banking, insurance, computer software development, retailing, investment, transportation, education, and translation.
It comprises a quality improvement process, which is generic in the sense that it can be applied to any of these activities and it establishes a behavior pattern, which supports the achievement of quality.
This in turn is supported by quality management practices which can include a number of business systems and which are usually specific to the activities of the business unit concerned.
In manufacturing and construction activities, these business practices can be equated to the models for quality assurance defined by the International Standards contained in the ISO 9000 series and the specified Specifications for quality systems. In the system of Company Quality, the work being carried out was shop floor inspection which did not reveal the major quality problems. This led to quality assurance or total quality control, which has come into being recently.




