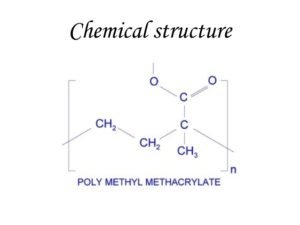
Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA)
Polymethylmethacrylate is also known as Acrylic or Acrylic glass. Shortly called PMMA. It is a transparent thermoplastic.
Physical Properties:
PMMA is a strong, tough, and lightweight material. It has a density of 1.17–1.20 g/cm3, which is less than half that of glass. It also has good impact strength, higher than both glass and polystyrene; however, PMMA’s impact strength is still significantly lower than polycarbonate and some engineered polymers. PMMA ignites at 460 °C (860 °F) and burns, forming carbon dioxide, water, carbon monoxide and low molecular-weight compounds, including formaldehyde.
PMMA transmits up to 92% of visible light (3 mm thickness), and gives a reflection of about 4% from each of its surfaces due to its refractive index (1.4905 at 589.3 nm). It filters ultraviolet (UV) light at wavelengths below about 300 nm (similar to ordinary window glass). Some manufacturers add coatings or additives to PMMA to improve absorption in the 300–400 nm range. PMMA passes infrared light of up to 2,800 nm and blocks IR of longer wavelengths up to 25,000 nm.
PMMA swells and dissolves in many organic solvents; it also has poor resistance to many other chemicals due to its easily hydrolysed ester groups. Nevertheless, its environmental stability is superior to most other plastics such as polystyrene and polyethylene, and PMMA is therefore often the material of choice for outdoor applications.
 Application & Uses:
Application & Uses:
Being transparent and durable, PMMA is a versatile material and has been used in a wide range of fields and applications such as rear-lights and instrument clusters for vehicles, appliances, and lenses for glasses. PMMA in the form of sheets affords to shatter resistant panels for building windows, skylights, bulletproof security barriers, signs & displays, sanitary ware (bathtubs), LCD screens, furniture and many other applications. It is also used for coating polymers based on MMA provides outstanding stability against environmental conditions with reduced emission of VOC. Methacrylate polymers are used extensively in medical and dental applications where purity and stability are critical to performance.